This is the thirtieth part of the ILP series. For your convenience you can find other parts in the table of contents in Part 1 – Boolean algebra
Hello! Today we are going to solve Sudoku using ILP.
Table of Contents
Description
In Sudoku we need to fill ![]() grid with numbers. In every column, in every row, and in nine smaller subgrids we can use every number from
grid with numbers. In every column, in every row, and in nine smaller subgrids we can use every number from ![]() to
to ![]() exactly once. We usually start with few fields filled and we need to find the rest. See the picture below (from wikipedia):
exactly once. We usually start with few fields filled and we need to find the rest. See the picture below (from wikipedia):
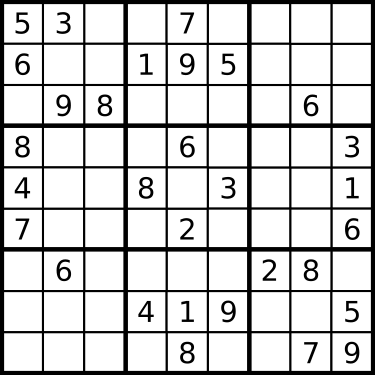
In this post we will use basic set operations a lot so make sure that you understand them.
Variables
Let’s start with variables for the problem. We usually use binary variables to indicate decision, however, this time we will use integer variables in range ![]() to represent the solutions. It is quite intuitive: after solving the problem we obtain the result by checking the value of variable for given board field. So we define the following variables:
to represent the solutions. It is quite intuitive: after solving the problem we obtain the result by checking the value of variable for given board field. So we define the following variables:
![]()
We also make sure that they are in the correct range:
![]()
Let’s now define constraints.
Constraints
This part is very easy. We already know how to define “all different” constraint, so all we need to do is to add constraints for every row, every column, and every subgrid:
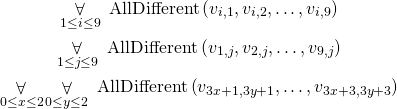
Code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
var board = new int[][]{ new int []{5,3,0,0,7,0,0,0,0}, new int []{6,0,0,1,9,5,0,0,0}, new int []{0,9,8,0,0,0,0,6,0}, new int []{8,0,0,0,6,0,0,0,3}, new int []{4,0,0,8,0,3,0,0,1}, new int []{7,0,0,0,2,0,0,0,6}, new int []{0,6,0,0,0,0,2,8,0}, new int []{0,0,0,4,1,9,0,0,5}, new int []{0,0,0,0,8,0,0,7,9} }; var width = board[0].Length; var height = board.Length; var solver = new CplexMilpSolver(new CplexMilpSolverSettings { IntegerWidth = 15, Epsilon = 0.1, StoreDebugExpressions = false, CacheConstants = false, StoreDebugConstraints = false }); Console.WriteLine("Create variables"); var fields = Enumerable.Range(0, height).Select(r => Enumerable.Range(0, width).Select(c => solver.CreateAnonymous(Domain.PositiveOrZeroInteger)).ToArray()).ToArray(); Console.WriteLine("Set ranges"); for(int row = 0; row < height;++row){ for(int column = 0; column < width; ++ column){ solver.Set<LessOrEqual>(fields[row][column], solver.FromConstant(9)); solver.Set<GreaterOrEqual>(fields[row][column], solver.FromConstant(1)); } } Console.WriteLine("Set known"); for(int row = 0; row < height;++row){ for(int column = 0; column < width; ++ column){ if(board[row][column] != 0)solver.Set<Equal>(fields[row][column], solver.FromConstant(board[row][column])); } } Console.WriteLine("Rows"); for(int row = 0; row < height;++row){ solver.Set<AllDifferent>(fields[row][0], fields[row].Skip(1).ToArray()); } Console.WriteLine("Columns"); for(int column = 0; column < width; ++ column){ solver.Set<AllDifferent>(fields[0][column], Enumerable.Range(1, height-1).Select(row => fields[row][column]).ToArray()); } Console.WriteLine("Quadrants"); for(int row = 0; row < height / 3;++row){ for(int column = 0; column < width / 3; ++ column){ var quandrant = Enumerable.Range(0, 3).SelectMany(i => Enumerable.Range(0, 3).Select(j => fields[row * 3 + i][column * 3 + j])).ToArray(); solver.Set<AllDifferent>(quandrant[0], quandrant.Skip(1).ToArray()); } } solver.AddGoal("goal", solver.FromConstant(0)); solver.Solve(); for(int row = 0; row < height;++row){ if(row % 3 == 0)Console.WriteLine("-------------"); for(int column = 0; column < width; ++ column){ if(column % 3 == 0)Console.Write("|"); Console.Write(solver.GetValue(fields[row][column])); } Console.Write("|"); Console.WriteLine(); } Console.WriteLine("-------------"); |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
Tried aggregator 1 time. MIP Presolve eliminated 7995 rows and 3969 columns. MIP Presolve modified 23909 coefficients. All rows and columns eliminated. Presolve time = 0.02 sec. (10.42 ticks) Root node processing (before b&c): Real time = 0.02 sec. (10.97 ticks) Parallel b&c, 8 threads: Real time = 0.00 sec. (0.00 ticks) Sync time (average) = 0.00 sec. Wait time (average) = 0.00 sec. ------------ Total (root+branch&cut) = 0.02 sec. (10.97 ticks) ------------- |534|678|912| |672|195|348| |198|342|567| ------------- |859|761|423| |426|853|791| |713|924|856| ------------- |961|537|284| |287|419|635| |345|286|179| ------------- |
Summary
As we can see, our toolkit for building ILP formulas is quite powerfull and we are able to solve Sudoku almost instantly just by translating rules of the game (nine different numbers in each column, nine different numbers in each row, nine different numbers in each subgrid) to mathematical operators.